networkx - community detection - label propagation(async)
line summary
- “label propagation”은 내 이웃들이 많이 속한 label이, 내 label이다, 라는 접근으로, 직관적인 개념에 기반하여 community을 만들어 나감.
async Label Propagation
- Label propagation은 “클래스가 식별되지 않은(unlabeled) 데이터 포인트에 클래스를 지정해주는 semi-supervised ML 알고리즘”을 말합니다. 특히, 아주 적은 수의 data들(혹은 Node)들만이 label을 가지고 있다고 한다면, 이 알고리즘을 통해, class를 증폭시켜줄 수 있죠. 아래 그림을 통해 보면 더 명확할 수 있는데, “내 커뮤니티는 내 이웃이 가장 많이 속한 커뮤니티와 같다”는 개념으로, 커뮤니티를 찾아나가는 방식이라고 보시면 됩니다.
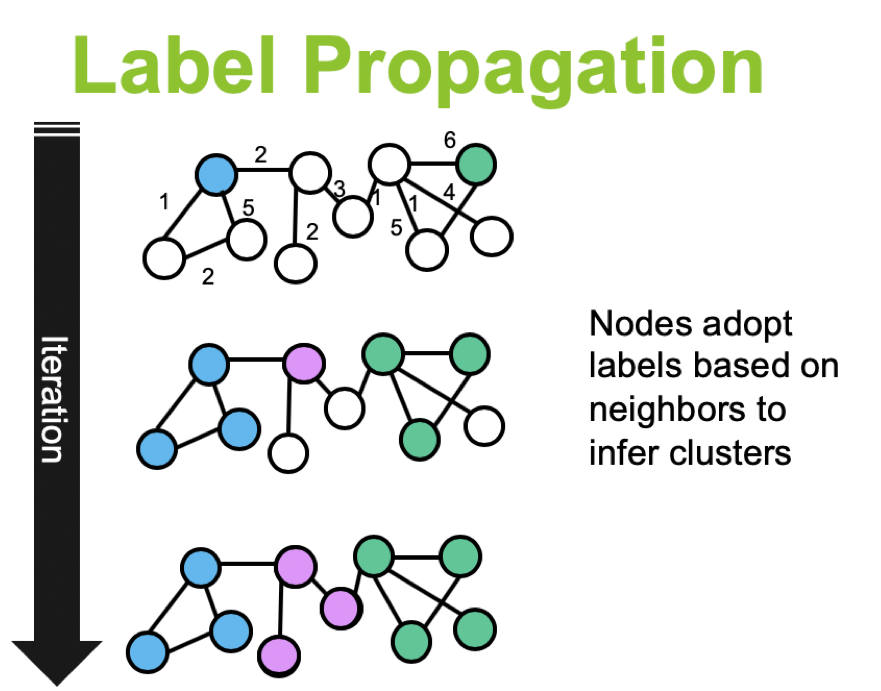
- Near linear time algorithm to detect community structures in large-scale networks에서 제시한 label-propagation 방법은 “비동기적(asynchrous)”인 방법, 즉 그냥, 그래프에서 노드를 하나하나씩 개선해나가는 방법입니다.
- 그 외로도, Community Detection via Semi-Synchronous Label Propagation Algorithms에서는 “반동기적인 방식으로, 속도뿐만 아니라, 안정성도 찾았다”라고 주장하고 있는데, 이 방법은 제가 나중에 다시 정리해볼게요.
Algorithm
1) initialize all node lable unique: 모든 노드에게 unique한 label을 부여함. 2) node shuffling: random성을 부여하기 위해서, node shuffling 3) node label update: 각 node의 label을, neighbor들에게서 가장 빈도가 높은 label로 업데이트 4) 종료조건 확인: “모든 node의 label”이 “neighbor에게서 가장 빈도가 높은 label”일 경우 종료. 아닐 경우 3)으로 - 여기서, 이 명제의 대우는 “최소한 한 node의 label이라도 다를 경우”이므로, 이를 체크.
- 매우 간단합니다. 호호. 그리고, 그냥 이미
networkx에 구현되어 있어서 그냥 그대로 써도 되기는 한데, 저는 한번 만들어봤습니다. 그래야, 알고리즘이 정확하게 이해되거든요.
import networkx
nx.algorithms.community.asyn_lpa_communities(G, seed=0)
Implement async LPA by myself.
- 따라서, graph
G로부터, label propagation을 통해서 비동기적으로 community를 뽑아내는, 함수를 다음과 같이 구현하였습니다.
def custom_asyn_lpa_communities(G):
"""
1) initialize all node lable unique: 모든 노드에게 unique한 label을 부여함.
2) random성을 부여하기 위해서, node shuffling
3) 각 node의 label을, neighbor들에게서 가장 빈도가 높은 label로 업데이트
4) "모든 node의 label"이 "neighbor에게서 가장 빈도가 높은 label"일 경우 종료. 아닐 경우 3)으로
- 여기서, 이 명제의 대우는 "최소한 한 node의 label이라도 다를 경우"이므로, 이를 체크.
nx.algorithms.community.asyn_lpa_communities(G, seed=0)
와 동일하나, random성때문에 완전히 같은 결과가 나오지는 않음.
"""
# 1) initialize all node lable unique
node_labels = {n: i for i, n in enumerate(G)}
# 이 알고리즘의 종료 조건은 "모든 노드의 label이 neighbor에서 가장 빈도가 높은 label일 경우 종료"
# 즉, "최소한, 한 노드라도 업데이트가 된다면, 3)으로 돌아가게됨 "
# 어떤 노드에서라도 업데이트가 발생하면 이를 True로 바꾸어 처리.
AT_LEAST_ONE_NODE_LABEL_CHANGE = True
while AT_LEAST_ONE_NODE_LABEL_CHANGE:
AT_LEAST_ONE_NODE_LABEL_CHANGE = False
# 2) node shuffling: random성을 주기 위해서 node의 순서를 섞음.
shuffled_nodes = list(G.nodes())
np.random.shuffle(shuffled_nodes)
# 3) Update each nodel label by max frequency-label of their neighbors
# node u의 이웃 중에서 가장 수가 많은 label이 u의 label.
# 동점자가 있을 경우 그 중에서 uniform-random-choice
for u in shuffled_nodes:
u_nbr = G[u]
if len(u_nbr) > 0:# neighbor이 없으면 label propagation이 불가능함.
# nbr_label_counter에 nbr의 label을 빈도 수로 정리함.
nbr_labels = [node_labels[v] for v in u_nbr]
nbr_label_counter = dict(collections.Counter(nbr_labels))
max_freq_label = max(nbr_label_counter.values())
# max_frequency를 가진 label이 1개라면 그 label로 바꿔야 하고.
# max_frequency를 가진 label이 1개 이상이면, 그중에서 random choose
best_labels = [k for k, v in nbr_label_counter.items() if v==max_freq_label]
choosed_label = np.random.choice(best_labels)
# 4) 어떤, 하나의 node라도 변경이 되었다면, 계속 진행함.
# 즉, node가 변경되었으므로, AT_LEAST_ONE_NODE_LABEL_CHANGE를 True로 업데이트.
if node_labels[u] != choosed_label:
node_labels[u] = choosed_label
AT_LEAST_ONE_NODE_LABEL_CHANGE = True
##################################################
# node_labels: dict(node -> label) 을
# label_to_nodes_dict: dict(label => [node, node])로 변경하여
label_to_nodes_dict = {}
for n, label in node_labels.items():
if label in label_to_nodes_dict:
label_to_nodes_dict[label].append(n)
else:
label_to_nodes_dict[label] = [n]
return list(label_to_nodes_dict.values())
댓글남기기