Java - Collection Interface
1 분 소요
Java - Collection interface
- Java에서는 미리 다양한 자료구조에 대한 Interface를 설계 해두었습니다. 관리의 용이성 혹은 method명을 표준화시켜 관리하는 것이 목적이겠죠.
Collection<E>: 동일한 type의 object들을 모아두는 container입니다. List<E>, Set<E>, Queue<E>, SortedSet<E>, Deque<E>는 Collection<E> interface를 상속받죠. 그리고, 자주 쓰이는 ArrayList는 List<E>를 상속받죠. 즉, 구조적으로 보면 Collection > List > ArrayList의 형태로 상속받는 것이죠. 여기서 T가 아닌 E가 쓰인 이유는 “Element”의 약자라서 그렇죠.-
Map<K, V>: K, V는 각각 Key, Value를 의미합니다. 즉, 그냥 값만 관리하는 것이 아니라, Key와 Value를 가리키는 형태로 데이터를 관리하고 싶을 때 사용하죠.
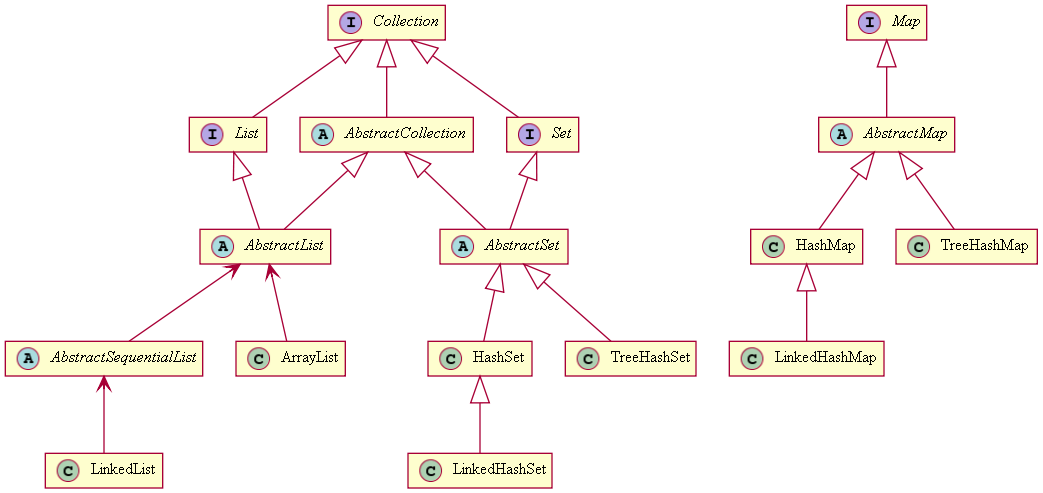
Methods in Collection Interface
Collection Interface에는 다음고 같은 method들이 선언되어 있습니다. 따라서, Collection을 상속받는 class들은 다음 method들을 정의해야 하죠. 모두 abstract method로 선언되어 있기 때문에, 상속받는 class에서 method들을 선언해주지 못하면, class를 구현할 수 없습니다.
int size(): 이 collection 내 원소의 수를 리턴boolean isEmpty(): 현재 collection이 비어 있는지 아닌지 확인하여 boolean을 리턴boolean contains(Object o): Object o가 현재 collection에 있는지 확인하여 boolean을 리턴boolean add(E e): Element e를 집어 넣고, 성공적으로 넣었으면 true를 티너, 아니면 false를 리턴boolean remove(Object o): Element e를 성공적으로 삭제하면 true를 티너, 아니면 false를 리턴boolean removeAll(Collection<> removeCollection) removeCollection에 있는 모든 값을 지웁니다.void clear(): collections의 모든 원소를 지웁니다.
- 직접 구현하지는 않아도,
ArrayList Object를 Collections Interface Variable이 가리키도록 할 수 있습니다. 이는 ArrayList가 Collection를 상속받기 때문에 가능한 것이죠. 그리고, 이미 구현된 Class이므로, 앞서 말한 모든 method들이 모두 구현되어 있습니다.
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Collection이 ArrayList의 상위 interface이므로
// 상위 interface variable로 하위 class Object를 가리킬 수 있습니다.
Collection<Integer> arrLst = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// Integer로 설정했으므로 Integer만 집어넣을 수 있습니다.
arrLst.add(1);
arrLst.add(2);
arrLst.add(3);
// forEach 과 lambda function을 이용해서 아래처럼 원소를 출력할 수도 있습니다.
arrLst.forEach(elem -> System.out.println(elem));
System.out.println("========================");
}
}

댓글남기기